About Compile
Code compilation refers to the process of converting a program
written in a high-level language (source code), understandable by humans,
into a machine language program that a computer can execute.
Compile Concept
Computers only understand binary code consisting of 0s and 1s,
necessitating the compilation of source code into machine language.
This process enables the computer to execute the program.
-
Programmer
High-level language
: Source code languages that are easier
for humans to understandC C++Java, Source Code etc.
-
Compiler
Software that converts the high-level
language into machine-readable languageC, C++, Java 01
-
Computer (CPU)
Machine language
: Language that machines can understand0 1

Compilation Stages
Code compilation involves a compiler software and typically follows four stages
-
Step 01 Source Code Writing
Writing the source code in a specific programming language
Easy for humans to understand but not directly executable
by a computer
-
Step 02 Compilation
Compiler processes the
written source codeAnalysis, checking for syntax errors, and translating into intermediate or machine code

-
Step 03 Linking
Some programming languages require a linking process after compilation
Source files combined into
a single executable file
(integrating modularized code
and linking libraries)
-
Step 04 Execution
Final compiled code
Converted into machine
language and executed
by the computer's CPU
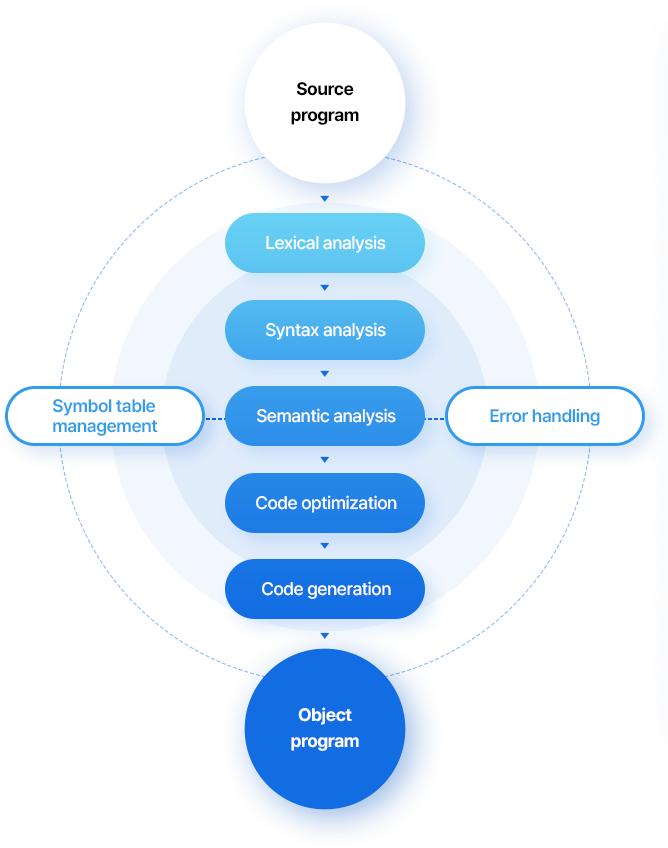
Detailed Compilation Process
The compiler analyzes and converts the source code,
creating an executable program through the steps listed below. The compiler detects errors at
each stage and performs optimization, enhancing the quality of the final executable code.
-
Source Program
-
Source code written by a programmer
-
Lexical Analysis
-
Breaking down the source code into a token stream
Removing spaces/comments and extracting identifiers,
operators, constants, etc.
-
Syntax Analysis
-
Checking the structure and syntax (grammar) of the source code
Converting the token stream into a parse tree or an abstract syntax tree (AST)
Generating error messages if grammatical errors are found
-
Semantic Analysis
-
Checking the meaning and intent of the code
Verifying variable definitions and uses, data type consistency, and function calls
Identifying code logic errors or integrity issues and reporting relevant errors
-
Symbol Table Management
-
Storing information defined in the source code such as variables, functions, constants, and data types; creating and managing tables to track and manage these identifiers
-
Error Handling
-
Processing and reporting errors that may occur during semantic analysis
Identifying errors for debugging and correction
-
Code Optimization
-
Optimizing code performance
Applying techniques such as removing duplicate code, constant folding, and eliminating unnecessary operations
Enhancing code execution speed and optimizing memory usage
-
Code Generation
-
Creating the final executable code
Compiler generates the target code based on the intermediate code or AST
Tailoring to specific hardware architecture or operating systems
-
Object Program
-
The final output that is executable, such as program files or libraries